Protecting the health of our feathered friends is paramount, and vaccination plays a vital role in ensuring their well-being. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of bird vaccination, covering everything from the importance of the process to the specifics of post-vaccination care. Understanding the different types of vaccines, proper administration techniques, and potential complications will empower you to make informed decisions and provide optimal care for your avian companions.
From identifying the appropriate vaccine for your bird’s species and age to recognizing and managing potential adverse reactions, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to successfully vaccinate your bird. It will walk you through the steps, offering clear instructions and safety precautions. This detailed approach to bird vaccination ensures a safe and effective process.
Introduction to Bird Vaccination

Vaccination programs are crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of bird populations. They play a vital role in preventing the spread of contagious diseases, which can significantly impact bird populations, leading to significant economic losses and ecological disruption. By proactively vaccinating birds, we can bolster their immune systems and mitigate the devastating effects of these diseases.Avian diseases encompass a wide spectrum of ailments, from mild infections to highly contagious and fatal conditions.
These diseases can be caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi. Examples include avian influenza (highly contagious and often fatal), Newcastle disease (another highly contagious viral disease), and various types of bacterial infections, which can all decimate flocks if left unchecked. The impact of these diseases extends beyond individual birds, affecting entire ecosystems and potentially impacting human health.
Understanding the nature and spread of these diseases is fundamental to implementing effective vaccination strategies.
Importance of Vaccination Programs
Vaccination programs provide a powerful defense against avian diseases. They can significantly reduce the prevalence and severity of outbreaks, protecting birds from devastating consequences. Vaccination programs, when properly implemented, can help maintain healthy bird populations, ensuring the long-term viability of bird species. Furthermore, well-planned vaccination strategies can contribute to the economic sustainability of poultry farming and other avian industries.
Preventive measures, such as vaccination, are more cost-effective than reactive measures, which often require extensive and costly treatments for affected birds.
Types of Bird Diseases
Bird diseases manifest in a variety of forms, impacting avian health in diverse ways. Some diseases are acute, rapidly progressing and often fatal, while others are chronic, lingering and debilitating. The specific symptoms and course of the disease depend heavily on the pathogen, the bird’s age, health status, and the virulence of the infection. Different diseases can be triggered by various factors.
- Viral Diseases: These are caused by viruses, and include highly contagious diseases like avian influenza and Newcastle disease. These viruses can spread rapidly through contaminated feed, water, or direct contact. Viral diseases often cause severe respiratory problems, neurological issues, and mortality. Avian influenza, for example, can have devastating effects on poultry flocks, causing significant economic losses.
- Bacterial Diseases: Bacterial infections, such as E. coli and Salmonella, can affect birds of all ages. These infections can be particularly problematic in young chicks and often lead to severe digestive problems, respiratory distress, and death. Proper hygiene practices and vaccination can significantly mitigate the risk of bacterial infections.
- Parasitic Diseases: These infections are caused by parasites such as mites, lice, and intestinal worms. Parasites can weaken birds, causing malnutrition and impacting their overall health. They can also spread easily, posing a threat to entire flocks. Effective parasite control measures, combined with vaccination, can help prevent the spread of parasitic diseases.
Benefits of Vaccination Programs
Vaccination programs offer several significant benefits to bird populations. They reduce the risk of disease outbreaks, thereby minimizing economic losses and protecting the environment. Vaccination programs also help safeguard human health by reducing the risk of zoonotic diseases, those that can be transmitted from animals to humans. The positive effects of these programs can be seen in the long-term health and well-being of avian populations.
- Reduced Mortality: Vaccination programs can drastically reduce mortality rates among birds by preventing the spread of deadly diseases. This translates into healthier bird populations and a lower economic burden.
- Economic Stability: By preventing outbreaks of costly diseases, vaccination programs help maintain the economic viability of poultry farming and other avian industries. Reduced treatment costs and the ability to maintain production are significant benefits.
- Environmental Preservation: Healthy bird populations are essential for maintaining ecological balance. Vaccination programs contribute to the preservation of biodiversity by reducing the risk of disease-related declines in bird populations.
Types of Bird Vaccines

Bird vaccination plays a crucial role in disease prevention and maintaining the health of avian populations. Understanding the different types of vaccines available and their appropriate administration methods is essential for effective disease control. This section details the various vaccine types, their administration methods, and the diseases they target.
Vaccine Types and Administration Methods
Various vaccine types are available for birds, each with its own characteristics and efficacy. These vaccines can be broadly categorized into live attenuated and inactivated vaccines. Live attenuated vaccines contain weakened forms of the pathogen, while inactivated vaccines contain killed pathogens.
Live Attenuated Vaccines
These vaccines use a weakened form of the pathogen to stimulate an immune response. The weakened virus replicates within the bird’s body, inducing an immune response without causing disease. Administration methods for live attenuated vaccines often involve oral administration or injection. Oral administration is generally preferred for certain species due to its ease of use. In some cases, intranasal administration may also be utilized.
The effectiveness of live attenuated vaccines often relies on the specific strain and the species of bird being vaccinated. However, they can potentially pose a risk if the attenuated virus reverts to its virulent form.
Inactivated Vaccines
Inactivated vaccines utilize killed pathogens to stimulate an immune response. These vaccines are generally safer than live attenuated vaccines, as they do not pose the risk of reversion to a virulent form. Inactivated vaccines are typically administered via injection. The effectiveness of inactivated vaccines is often dependent on the adjuvant used to enhance the immune response.
Comparison of Vaccine Types
The choice of vaccine type depends on several factors, including the specific disease being targeted, the species of bird, and the desired level of protection. Live attenuated vaccines often provide a longer-lasting immunity, but the risk of reversion to virulence needs careful consideration. Inactivated vaccines are generally safer, but the immune response may be less robust and require booster shots for optimal protection.
Table of Vaccine Types
| Vaccine Type | Administration Method | Target Diseases |
|---|---|---|
| Live attenuated Newcastle Disease Vaccine | Oral, Intranasal, or Injection | Newcastle Disease |
| Inactivated Infectious Bursal Disease Vaccine | Injection | Infectious Bursal Disease (Gumboro Disease) |
| Live attenuated Avian Influenza Vaccine | Injection | Avian Influenza |
| Inactivated Avian Pox Vaccine | Injection | Avian Pox |
Choosing the Right Vaccine
Selecting the appropriate avian vaccine is crucial for the health and well-being of your feathered companions. Factors such as the specific bird species, its age, and potential health conditions all play a significant role in determining the most effective and safe vaccine protocol. A veterinarian’s expertise is invaluable in making informed decisions, ensuring the vaccine aligns with the bird’s individual needs.
Factors Influencing Vaccine Selection
Understanding the nuances of different bird species is paramount in choosing the correct vaccine. Different avian species exhibit varying susceptibilities to specific diseases, requiring tailored vaccine approaches. Consideration of the bird’s age is also critical, as certain vaccines may be more effective at different life stages. Age-related factors in birds, like their immune system development and physiological changes, influence vaccine responses.
Young birds may require different vaccine formulations than mature adults. A veterinarian can assess the bird’s overall health and medical history to ensure the chosen vaccine aligns with its particular needs.
Role of Avian Species in Vaccine Selection
Different bird species possess distinct susceptibility profiles to various diseases. For example, budgies are susceptible to psittacine beak and feather disease, whereas chickens are vulnerable to infectious bronchitis. Selecting a vaccine tailored to the specific bird species ensures the vaccine’s effectiveness and prevents potential adverse reactions. Consequently, a vaccine designed for one species may not be suitable for another.
A thorough understanding of the bird’s species-specific vulnerabilities and requirements is essential.
Role of Bird Age in Vaccine Selection
Avian age significantly impacts vaccine selection. Young birds often have developing immune systems, requiring different vaccine formulations and dosages than mature adults. Furthermore, the bird’s age influences its physiological condition and response to vaccination. Avian immune responses differ between hatchlings, juveniles, and adults, and the choice of vaccine must account for these differences. A veterinarian can assess the bird’s age-related factors to optimize vaccine efficacy and minimize potential risks.
Importance of Consulting with a Veterinarian
Consulting with a qualified avian veterinarian is paramount in selecting the right vaccine for your bird. Veterinarians possess the specialized knowledge and experience necessary to evaluate your bird’s unique circumstances and tailor the vaccination protocol to meet its specific needs. They can diagnose any underlying health conditions that may influence vaccine selection. They can also offer advice on the best timing for vaccination and the potential side effects of different vaccines.
This personalized approach minimizes potential risks and maximizes the effectiveness of the chosen vaccine.
Flowchart for Choosing the Appropriate Vaccine
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the bird’s species and age. |
| 2 | Consult with a qualified avian veterinarian. |
| 3 | Provide detailed medical history of the bird. |
| 4 | Discuss potential health concerns and risk factors. |
| 5 | Obtain recommendations for suitable vaccines from the veterinarian. |
| 6 | Review potential side effects and risks. |
| 7 | Administer the vaccine following the veterinarian’s instructions. |
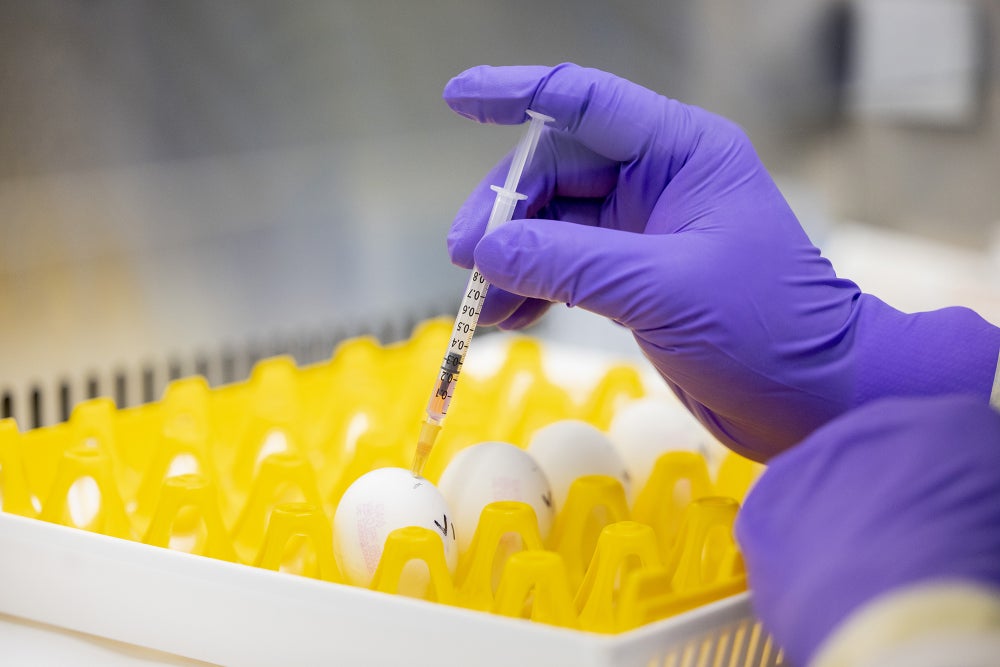
Vaccine Administration Procedures
Proper vaccination techniques are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and safety of the procedure for avian patients. Incorrect administration can lead to poor immune response, vaccine failure, or even complications for the bird. Following a standardized protocol is essential for optimal results and minimizing potential risks.Effective vaccination involves more than just injecting the vaccine; it also necessitates meticulous attention to detail in preparation, handling, and post-vaccination care.
This section details the proper procedures for various vaccine administration methods, highlighting safety precautions and potential complications.
Injectable Vaccine Administration
Injectable vaccines, commonly used for birds, require precise technique to ensure accurate dosage and minimize tissue damage. Different vaccine types might have specific instructions regarding injection sites and needle gauges.
- Selection of Injection Site: The appropriate injection site varies based on the bird species and size. Avoid areas with vital organs or blood vessels. Common sites include the pectoral muscles or the thigh muscles, ensuring that the area is clean and free of any feather or debris. The injection site should be easily accessible without causing undue stress to the bird.
- Preparation of the Vaccine: Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions regarding the preparation of the vaccine, ensuring the correct dilution and temperature of the vaccine. Use sterile equipment and solutions throughout the process. Improper preparation can render the vaccine ineffective or potentially harmful.
- Administration Technique: Employ aseptic techniques throughout the procedure. Use a needle and syringe appropriate for the bird’s size and the vaccine type. Insert the needle at a 45-degree angle, injecting the vaccine slowly and carefully. Avoid injecting too quickly or forcefully to prevent tissue damage. Ensure the correct dose is administered as per the recommended dosage guidelines.
After injection, gently massage the area to help distribute the vaccine evenly.
- Post-Injection Care: Monitor the bird for any adverse reactions, such as swelling, redness, or lethargy. Provide appropriate care, including adequate hydration and nutrition, and observe for signs of distress. Isolate the bird from other birds for a few days to prevent the spread of any potential infection.
Oral Vaccine Administration
Oral vaccines, often used for specific diseases, present a different approach to vaccination. The process necessitates careful handling to ensure the vaccine reaches the intended location and is consumed by the bird.
- Vaccine Preparation: Prepare the vaccine according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring the appropriate concentration and form for oral administration. The vaccine should be in a palatable form, such as a paste or a solution mixed with feed.
- Administration: Offer the vaccine-containing feed or solution to the bird in a manner that ensures consumption. The bird should be able to access and ingest the vaccine without difficulty. Observe the bird to ensure it ingests the appropriate amount of vaccine. Do not force the vaccine.
- Monitoring: Monitor the bird for any adverse reactions or complications. Provide appropriate care and hydration. Observe for signs of distress. Do not allow other birds to consume the vaccine-containing feed or solution.
Table of Vaccine Administration Steps
| Step | Description | Image Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gather all necessary materials, including sterile needles, syringes, and appropriate vaccine. Ensure proper lighting for clear visibility. | A well-organized workspace with all the required equipment, needles, syringes, and vaccine vials. |
| 2 | Prepare the bird by gently restraining it. Identify a suitable injection site, ensuring it is clean and free of feathers. | A bird gently restrained, and the injection site is clearly visible and clean. |
| 3 | Prepare the vaccine according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Verify the correct dosage and solution. | The prepared vaccine in the syringe and a visual confirmation of the correct dosage and solution. |
| 4 | Inject the vaccine slowly and precisely into the designated site, ensuring the correct angle and depth. | The injection process with the needle at the appropriate angle, demonstrating a smooth injection into the chosen site. |
| 5 | Monitor the bird for any adverse reactions. Provide appropriate post-vaccination care. | The bird is being observed for any adverse reaction, and appropriate care is being provided. |
Post-Vaccination Care
Proper post-vaccination care is crucial for the well-being and successful immune response of vaccinated birds. This phase involves monitoring the birds closely for any adverse reactions and providing supportive care to ensure a smooth recovery. Careful observation and prompt intervention can significantly reduce potential complications and ensure the bird’s full recovery.
Importance of Post-Vaccination Monitoring
Post-vaccination monitoring is vital for detecting and managing any adverse reactions that may occur. Early detection of complications allows for timely intervention, minimizing discomfort and potentially preventing more serious problems. By closely observing the birds, avian veterinarians can assess the efficacy of the vaccine and identify potential issues with the administration process. This proactive approach ensures that the vaccination process remains safe and effective for all birds.
Signs of Adverse Reactions
Several signs can indicate adverse reactions to vaccination. These reactions may range from mild discomfort to severe complications. Recognizing these signs is critical for appropriate management.
- General malaise, including lethargy, reduced activity, and appetite loss, are common signs of systemic reactions. A decrease in energy levels or a lack of interest in usual activities should be noted.
- Local reactions at the injection site, such as swelling, redness, or tenderness, are frequently observed. Careful examination of the injection site is important for early identification.
- Fever, characterized by elevated body temperature, can be a sign of a more serious systemic response. Monitoring body temperature is crucial in these cases.
- Respiratory distress, such as labored breathing or difficulty in breathing, may indicate a severe reaction. Any changes in breathing patterns should be immediately noted.
- Neurological signs, such as tremors, seizures, or paralysis, are serious concerns. Prompt veterinary intervention is essential for these conditions.
- Diarrhea or vomiting can also be observed. This may suggest an upset stomach related to the vaccine or a separate infection.
Management of Adverse Reactions
Appropriate management strategies depend on the severity and nature of the adverse reaction. Veterinary advice is essential for managing potential complications. It is important to note that managing adverse reactions can require specific treatments and care tailored to the bird’s needs.
- Mild reactions, such as localized swelling or slight lethargy, often resolve on their own with supportive care. This might include providing a comfortable environment, offering fresh water and nutritious food, and monitoring the bird for any worsening signs.
- For more severe reactions, such as fever or respiratory distress, veterinary intervention is necessary. Prompt consultation with a veterinarian is critical to receive appropriate medical care and treatment.
- Neurological signs require immediate veterinary attention. These situations demand prompt intervention to stabilize the bird and prevent further complications.
Monitoring Procedures After Vaccination
Post-vaccination monitoring should be conducted over a specified period. This involves regular observations of the birds’ overall health and well-being. A consistent monitoring plan can ensure any potential complications are addressed promptly.
- Regular visual inspections of the birds are essential for detecting any physical changes or abnormalities. Look for any changes in posture, breathing, or behavior.
- Monitoring the birds’ appetite, hydration, and stool consistency is critical. Any changes in these parameters can indicate potential problems.
- Temperature checks, when necessary, should be done to monitor for fever. Following a standardized procedure for taking the bird’s temperature is important.
- Detailed records of observations, including dates, times, and specific signs, are valuable for tracking the bird’s response to vaccination. Keeping accurate records allows for effective communication with the veterinarian.
Potential Adverse Reactions and Management Strategies
| Adverse Reaction | Symptoms | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Local Swelling | Inflammation at the injection site | Monitor closely; apply a warm compress if appropriate; seek veterinary advice if swelling worsens. |
| Lethargy | Reduced activity, appetite loss | Provide a quiet, comfortable environment; offer fresh water and nutritious food; monitor for worsening symptoms. |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature | Provide cool water; monitor closely; seek veterinary advice if fever persists or worsens. |
| Neurological Signs | Tremors, seizures, paralysis | Seek immediate veterinary attention. |
| Respiratory Distress | Labored breathing, difficulty breathing | Seek immediate veterinary attention. |
Preventing Vaccine-Related Issues

Proper vaccination protocols are crucial for avian health. Minimizing potential complications, such as adverse reactions or stress-induced illness, is essential for successful vaccination programs. This section details crucial steps to mitigate vaccine-related issues, ensuring the well-being of your feathered companions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Vaccine Administration
Careful technique is paramount in vaccine administration. Common errors can lead to unnecessary discomfort or even injury to the bird. Incorrect injection sites, improper needle gauge for the bird’s size, and insufficient restraint can all contribute to complications. Understanding the bird’s anatomy and appropriate handling techniques is essential. Over-handling, for example, can increase stress levels, potentially hindering the immune response.
- Verify the correct injection site. Using a site that is not appropriate for the vaccine or the bird’s size can lead to pain and discomfort. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and veterinary recommendations for accurate placement.
- Ensure the needle gauge is suitable. Using a needle that is too large for the bird can cause tissue damage and hemorrhage. Conversely, a needle that is too small may not reach the intended muscle, leading to ineffective vaccination.
- Employ appropriate restraint techniques. Gentle but firm handling is necessary to maintain the bird’s stability without causing harm. Excessive force can lead to stress and injuries, impacting the bird’s health.
- Maintain proper hygiene. Cleanliness is vital. Sterile equipment and a hygienic environment minimize the risk of infection following vaccination.
Preventing Stress and Injury to Birds During Vaccination
Minimizing stress during the vaccination process is crucial for a successful immune response. Birds are highly sensitive to stress, which can negatively impact their overall health and hinder the vaccine’s effectiveness.
- Minimize handling time. Brief and gentle handling is key. Keep the bird contained in a calm, quiet environment. Minimize noise and distractions.
- Use proper restraint techniques. Gentle but firm restraint is critical to prevent injuries. Avoid sudden movements or harsh handling.
- Maintain a calm atmosphere. A tranquil environment can greatly reduce stress. Minimize noise and other potential stressors. Use calming music or sounds to create a relaxed environment.
- Provide adequate pre- and post-vaccination rest. Allow the bird ample time to recover and adjust to the vaccination process. Rest and recovery are vital for the bird’s well-being.
Importance of Proper Storage and Handling of Vaccines
Proper storage and handling of vaccines are critical for maintaining their potency. Incorrect handling can diminish the vaccine’s effectiveness, rendering it useless.
- Adhere to storage guidelines. Ensure vaccines are stored at the recommended temperature and humidity levels. Temperature fluctuations can significantly compromise the vaccine’s potency.
- Use aseptic techniques. Sterile equipment and procedures prevent contamination and maintain vaccine integrity.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions. Proper storage, handling, and administration protocols are crucial for effective vaccine delivery.
- Discard expired vaccines. Using outdated vaccines can be detrimental to the bird’s health. Dispose of expired vaccines appropriately.
Vaccine Administration Checklist
This checklist ensures a systematic approach to bird vaccinations, minimizing risks and maximizing success.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gather all necessary supplies (vaccine, syringes, alcohol swabs, restraint tools, record book). |
| 2 | Prepare the vaccination area, ensuring cleanliness and quietness. |
| 3 | Identify the appropriate injection site, consulting relevant resources. |
| 4 | Restraint the bird gently and calmly. |
| 5 | Check the vaccine’s expiration date and proper storage conditions. |
| 6 | Administer the vaccine using the correct technique and needle gauge. |
| 7 | Record the vaccination date, vaccine type, and any observations. |
| 8 | Allow the bird ample rest period after vaccination. |
Resources for Further Information
Staying informed is crucial for successful bird vaccination. Properly understanding the nuances of avian health and vaccination protocols is essential for the well-being of your feathered companions. This section provides valuable resources for continued learning and research.
Reputable Organizations and Veterinary Websites
Numerous organizations and veterinary websites offer comprehensive information on avian health and vaccination. These resources can provide detailed guidelines, current research, and best practices. Consulting these sources ensures you’re using the most up-to-date and accurate information.
- American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA): The AVMA is a professional organization for veterinarians, offering resources on avian health, including vaccination protocols. Their website often includes guidelines for various species, covering important aspects like disease prevention and treatment.
- The Avian Health Network: This online community provides a platform for sharing information, asking questions, and connecting with avian veterinarians and enthusiasts. It’s a valuable resource for discussing specific concerns and seeking expert advice.
- The American Poultry Science Association (APSA): For poultry-specific information, the APSA offers insights into avian health and vaccination, including research articles and publications. Their expertise is particularly valuable for those involved in poultry farming or raising poultry for personal consumption.
- Veterinary clinics specializing in avian medicine: Locating a veterinarian specializing in avian medicine is crucial. These clinics are well-versed in the specific needs of birds, offering vaccination recommendations tailored to individual species and health conditions.
Credible Websites for Bird Vaccination
Reliable online resources offer comprehensive information on bird vaccination. These sites are carefully curated to ensure accuracy and facilitate a deeper understanding of avian health.
- Specific avian veterinary websites: Look for websites maintained by avian veterinarians or avian-focused veterinary clinics. These sites often contain detailed information on vaccination protocols, relevant diseases, and species-specific guidelines.
- University extension services: Many universities offer extension services focused on animal health. These resources often provide practical information and guidelines for avian vaccination in various settings, from backyard bird owners to large-scale breeders.
- Reputable bird breeders and organizations: Experienced bird breeders and organizations dedicated to avian welfare frequently share insights into avian health and vaccination. These resources can provide practical advice based on real-world experience and observations.
Bird Vaccination Guidelines and Articles
Access to up-to-date guidelines and articles is essential for informed decision-making. These resources provide a deeper understanding of the scientific basis for bird vaccination.
- Scientific journals: Publications like the “Journal of Avian Medicine and Surgery” offer detailed research on avian diseases and vaccination strategies. These articles often provide in-depth information on the efficacy and safety of various vaccines.
- Veterinary textbooks: Veterinary textbooks dedicated to avian medicine provide comprehensive coverage of vaccination protocols and their application in various species. These resources are invaluable for a thorough understanding of the subject.
- Guidelines from avian health organizations: Specialized avian health organizations frequently release guidelines on vaccination practices. These guidelines provide comprehensive recommendations for different avian species and health situations.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, this guide has provided a thorough examination of bird vaccination, encompassing crucial aspects from disease prevention to post-vaccination care. By understanding the different vaccine types, proper administration techniques, and potential complications, you can confidently vaccinate your bird while minimizing risks. Remember to prioritize the health and well-being of your avian companion throughout the entire process. A proactive approach to bird vaccination is essential for maintaining the health and longevity of your feathered friend.